Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to find out the antimicrobial activities of
Figures & Tables
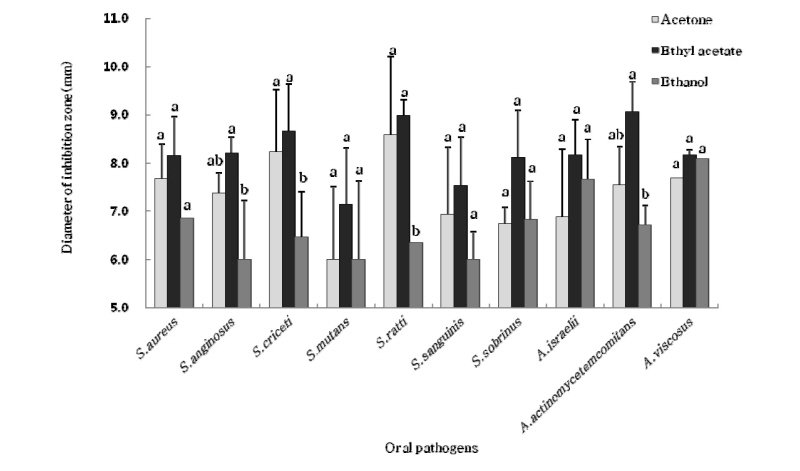
Antimicrobial activity of extracts from Ramaria botrytis by disc diffusion. The results represent the Mean±SD of values obtained from three independent experiments. Mean with different letter (a-b) on the bars in the same bacteria are significantly different by Duncan's multiple comparison (p<0.05)


