Abstract
Objectives: Calcium hydroxide, a root canal temporary sealer, has long been used and it has anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory activity. To investigate the properties of a newly developed calcium hydroxide paste comprising silicon-substituted hydroxyapatite (Si-HA), we examined the anti-inflammatory activity of the new calcium hydroxide paste in RAW 264.7 macrophages stimulated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS), which causes infection of the root canal. Methods: The test materials, including Calcipex II as control group and the newly developed TRC paste, were extracted from cell culture media and then diluted for experiment. In LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells, the cytotoxicity and nitric oxide (NO) production of test materials were measured by MTT assay and Griess reagents, respectively. Also, the expression of the inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) was assessed by western blotting. Results: The IC50 values of Calcipex II and TRC paste were 17.6 ㎎/㎖ and 13.5 ㎎/㎖, respectively. The level of NO, increased by LPS, was dose-dependently inhibited more by TRC paste than Calcipex II treatment. In addition, iNOS expression was decreased by 71% and 92% at concentrations of 2 ㎎/㎖ and 20 ㎎/㎖ of TRC paste, respectively. Conclusions: We demonstrated that the Si-HA calcium hydroxide paste has a slightly improved anti-inflammatory property and further studies are needed before clinical recommendations are proposed.
Figures & Tables
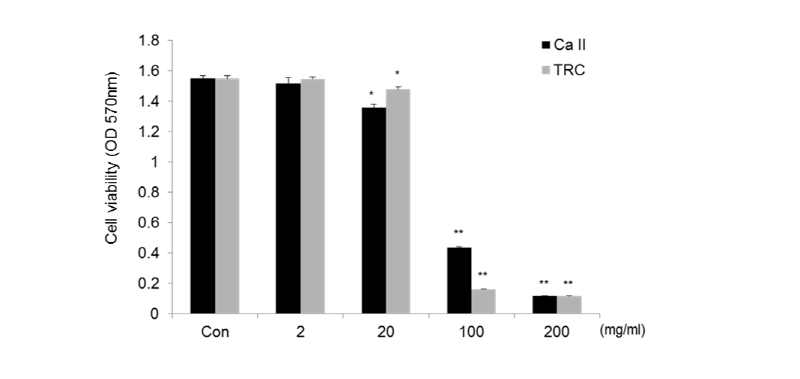
Fig. 1. MTT assay for the viability analysis of RAW 264.7 cells treated with various concentrations of Calcipex II or TRC paste for 24 h. Absorbance was read at 570 nm, and data are expressed as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 versus untreated cells (Con).


