Abstract
Objectives: This study aims to prove that stress directly or indirectly affects the jaw joint disorders and provide basic data for developing oral health promotion program. Methods: The study was conducted by distributing a questionnaire survey to more than 350 people from December 30, 2016 to January 7, 2017. Among them, 336 copies were collected and 314 copies were utilized eventually, except Section 314, for the final analysis. Regression analysis was performed to investigate the factors affecting temporomandibular joint disorders. Results: As a result, academic achievement and stress were found to affect the temporomandibular joint disorders. The higher the level of education and stress, the higher the subjective symptoms of jaw joint disorder. Conclusions: Because stress affects temporomandibular joint disorders, it is necessary to find out the cause of stress not only for professional treatment but also for solution of temporomandibular disorder. Thus, stress level must be conisdred as influential factors in developing a jaw joint disease prevention program.
Figures & Tables
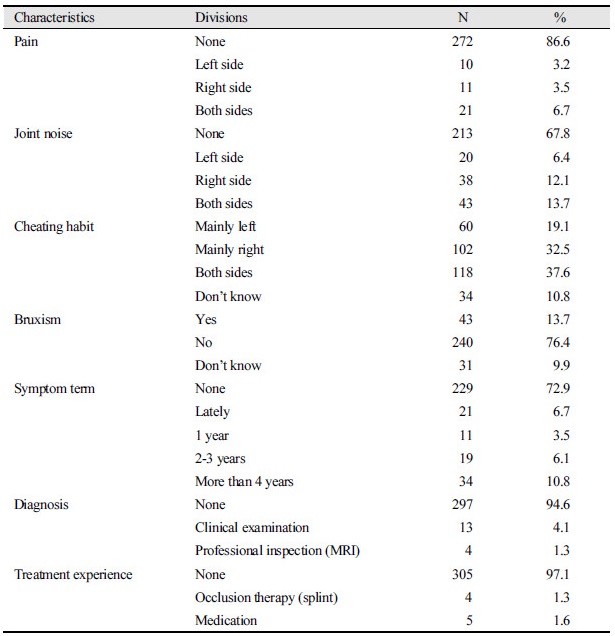
Table 1. Subjective symptoms of jaw joint disorders


