Abstract
Objectives: The purpose of this study is to provide basic data on the continuous management and institutional measures in the future by understanding the research trends of patient safety in healthcare field. Methods: The data were extracted from 2011-2016 KoreaMed, KMBase, KISS, NDSL and KISTI. Data were analysis by frequency analysis using the SPSS 14.0 program. Results: 87.0% of the studies were quantitative studies. As for the method of sampling, ‘No use’ was the highest at 56.5%. Most of the participants in the study were ‘nurses’ (50.7%). 19 hospitals (35.8%) were the most common. The subjects of the study consisted of 35 (51.5%) patients’ safety culture (awareness) and 20 (29.4%) ‘safety nursing activities’. Conclusions: Patient safety and patient safety should be maintained. Further, a mature patient safety culture should be settled through cooperation management among medical staff.
Figures & Tables
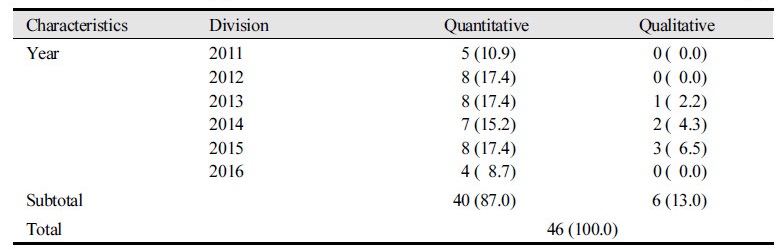
Table 1. Research status by year Unit:N (%)


