Abstract
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to review depression and anxiety associated with pain during scaling procedures, and to establish measures for reducing scaling pain encompassing not only physical factors but also psychological aspects of patients. This study also attempts to reduce anxiety through proper patient education prior to scaling procedures. Methods: In Seoul, and Gyeonggi area from July 26, 2017 to August 19, 2017, there were 327 copies of questionnaire data collected, excluding 23 questionnaires with insufficient information such as missing entries. The following inductions were made based on data collected. Results: There are positive correlations between pain and depression, dental anxiety, trait anxiety, and state anxiety. Especially, stronger correlation is present between pain and dental anxiety. Depression (β= 0.439, p<0.001) is the most influential factor associated with pain. Next is dental anxiety (β=0.292, p< 0.001). Higher the depression and dental anxiety tend to increase pain over scaling procedure. This model is with adjusted explanatory power of 28.2%. Conclusions: The result demonstrates that there is a correlation between scaling pain and depression, dental anxiety, trait anxiety, and state anxiety. Especially, depression and dental anxiety were prominent factors in affecting scaling pain. Therefore, considering aforementioned- findings, a dental hygienist's positive attitude may help in reducing the pain of the patient during scaling procedures, by affecting the psychological state of the patient and reduce the anxiety through proper education prior to scaling procedures.
Figures & Tables
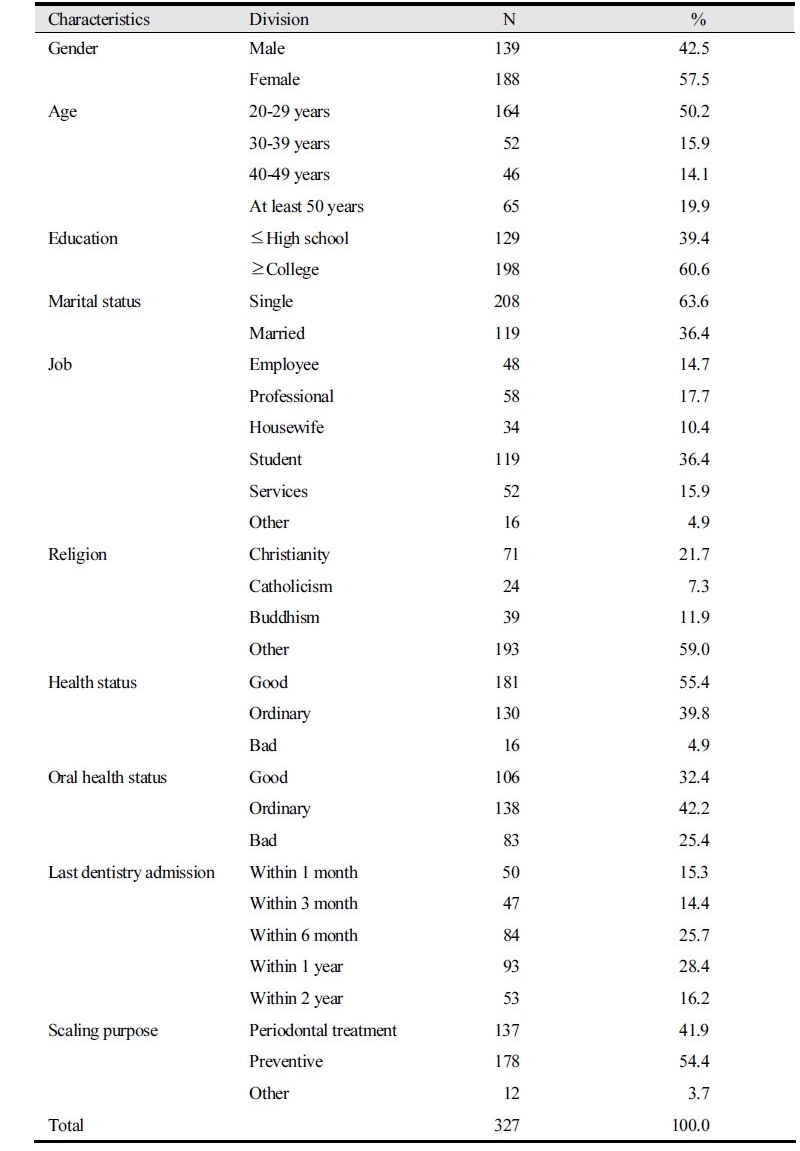
Table 1. General characteristics of the subject


