Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to examine factors influencing satisfaction with clinical practice in dental hygiene students. Through this study, we suggested efficient guidance to increase satisfaction levels with clinical practice. Methods: A self-reported questionnaire was filled out by 235 students of clinical dental hygiene in Seoul⋅Gyeonggi⋅Chungcheong⋅Kyongsang and Jeolla province from June 9 to 30, 2017. The questionnaire consisted of questions on general characteristics (6 items), clinical practice characteristics (7 items), ego-resilience (14 items), family support (24 items), teaching effectiveness(35 items), and clinical practice satisfaction (30 items). Data were analyzed using SPSS 19.0. One way ANOVA, the Scheffe Post-hoc test, and the Pearson correlation coefficients were reviewed, and a multiple regression analysis was conducted. Cronbach’s alpha of ego-resilience, family support, teaching effectiveness, clinical practice satisfaction were 0.784, 0.892, 0.954 and 0.935, respectively. Results: ego-resilience was 3.24 points, family support was 3.24 points, teaching effectiveness was 2.93 points, clinical practice satisfaction 3.44 points. The meaningful variables which influenced clinical practice satisfaction were the ego-resilience, family support and teaching effectiveness. These factors explained 40.6% of the variance in clinical practice satisfaction. Conclusions: One of the most significant predictors of clinical practice satisfaction in dental hygiene students was teaching effectiveness. Therefore, a teaching program to improve eaching effectiveness should be developed and applied.
Figures & Tables
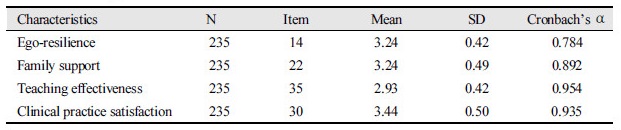
Table 1. Reliability of instrument scales


