Abstract
Objectives: The study aimed to identify the oral health factors that affect the nutritional status of the elderly. Methods: The study was conducted over ten months from September 2013 to June 2014, and included senior citizens who were supported by the visiting health service. The rate of saliva release, the number of remaining teeth, and the ability of the elderly to identify nutritional conditions were evaluated. Statistical analyses were performed using the t-test, ANOVA, and multiple linear regression using SAS 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA.). Results: The study participants had an average irritation saliva secretion rate of 2.26 ± 1.11 mg per minute. The higher the rate of saliva secretion, the higher the mini nutritional assessment (MNA) score (p<0.001). The average number of remaining teeth was 8.21 ± 9.76. The MNA scores were highest in groups with 11 or more remaining teeth (p=0.001). The factors that affected the nutritional condition of the elderly were their ability to perform activities of daily living, saliva flow rate, and number of remaining teeth. The highest correlation among them was that of the standardized regression coefficient was – 0.386 by activity daily living , followed by a 0.170 saliva secretion rate and 0.118 remaining teeth in daily life performance. Conclusions: Activities of daily living and rate of saliva secretion showed the highest correlations to nutritional status of the elderly.
Figures & Tables
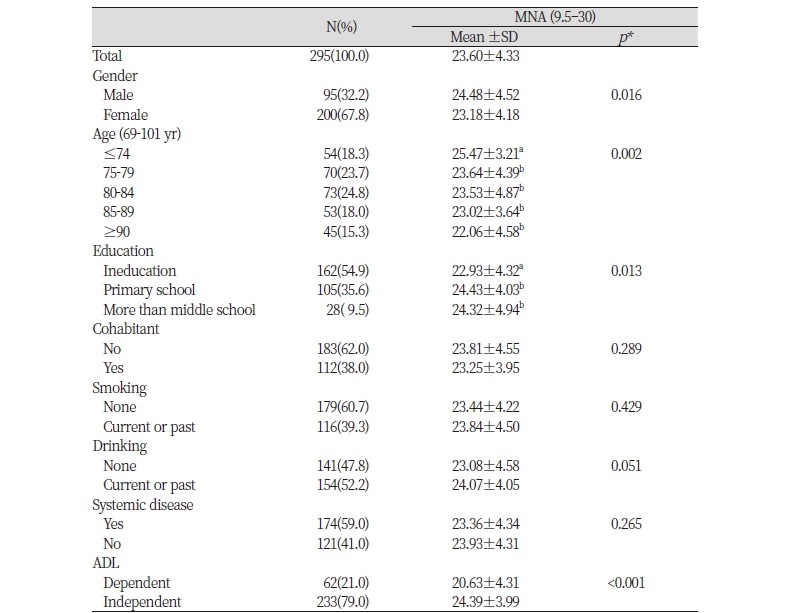
Table 1. MNA score according to socioeconomic characteristics and ADL of subjects


