Abstract
The study aimed to investigate the relationship between depression and number of present teeth in Korean elderly individuals. Data for this cross-sectional survey was obtained from the records of the sixth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). The subjects were 1,199 Korean elderly individuals above 65 years of age. The survey and examination data were used for the independent variables. The KNHANES included health status, nutrition survey, and oral examination. x2-test was performed to identify the characteristics of depression and number of teeth present according to the characteristics of the study subjects. Logistic regression analysis was also performed to identify the relationship between depression and number of teeth present. The statistical significance level wa sset at 0.05. The prevalence of depression in the subjects was 14.8%. There were statistically significant differences in the prevalence of depression, depending on gender (p<0.001), education level (p=0.001), income (p=0.001), spouse status (p<0.001), and alcohol consumption (p=0.020). The association between depression and the number of teeth present showed statistically significant difference after adjustment (p=0.040). Depression in elderly individuals was closely related to the number of teeth present. Therefore, public health policies for improving oral health should be established to prevent depression.
Figures & Tables
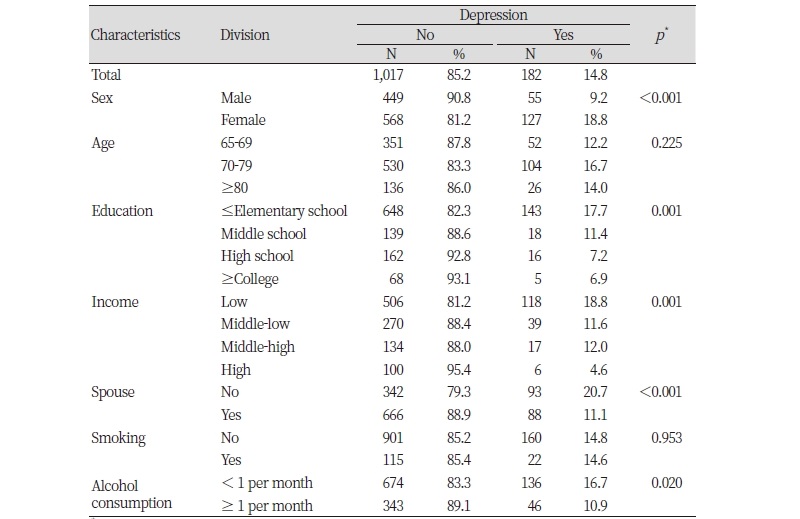
Table 1. Depression according to demographic distribution


