Abstract
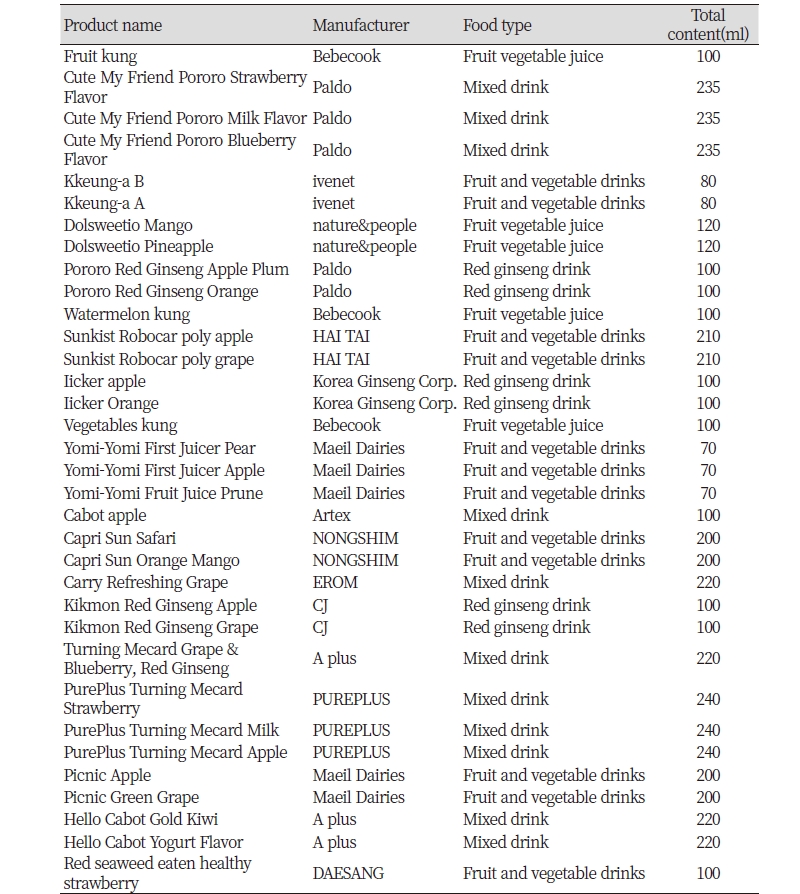
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to analyze the risk of dental caries and erosion associated with beverage consumption by measuring the sugar content and acidity of beverages for children, marketed in general food stores and cooperative living associations in Korea. Methods: Sixty types of children's beverages marketed in Korea were selected for the study. Calories, sodium, and carbohydrates in the nutrients per 100 ml, the sugar content, and pH of each beverage were measured. Frequency analysis, independent t-test, and one-way ANOVA were performed (
Figures & Tables