Abstract
The purpose of this study was to compare SYBR Green qPCR, TaqMan, and bacterial selective medium cultures for accurate quantitative analysis of oral microorganismsThe SYBR Green method is widely used to analyze the total amount of oral microorganisms in oral saliva. However, in this study, MTR-PCR method based on TaqMan method was performed using newly developed primers and probes. In addition, it was designed to confirm the detection agreement of bacteria among bacteria detection method.As a result of MRT-PCR and SYBR Green qPCR analysis, more than 40 times (0.9-362.9 times) bacterium was detected by MRT-PCR. In addition, more bacteria were detected in saliva in the order of MRT-PCR, SYBR Green qPCR, and bacterium culture, and the results of MRB-PCR and SYBR Green qPCR showed the highest agreement. The agreement between the three methods for detecting P. intermedia was similar between 71.4 and 88.6%, but the agreement between MRT-PCR and SYBR Green qPCR was 80% for S. mutans. Among them, the number of total bacteria, P. intermedia and S. mutans bacteria in saliva was higher than that of SYBR Green qPCR method, and bacterium culture method by MRT-PCR method. P. intermedia and S. mutans in saliva were detected by MRT-PCR and MRT-PCR in 88.6% of cases, followed by the SYBR Green qPCR method (80.0%).The SYBR Green qPCR method is the same molecular biology method, but it can not analyze the germs at the same time. Bacterial culturing takes a lot of time if there is no selective culture medium. Therefore, the MRT-PCR method using newly developed primers and probes is considered to be the best method.
Figures & Tables
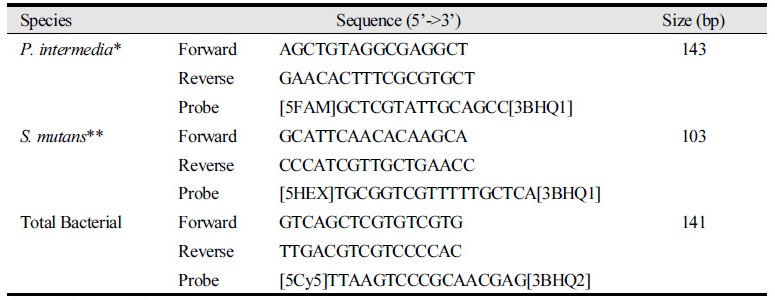
Table 1. Nucleotide sequence and reaction conditions of real-time quantitative PCR primer using MRT-PCR method


