Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study is to investigate the mechanical properties and antibacterial effects on Streptococcus mutans of composite resins containing phytoncide. Methods: Phytoncide was mixed with commercial composite resins at 0 (control), 1.25, 2.5, 3.75, and 5.0 weight percentage (wt%). Mechanical properties related to composite resins such as surface hardness, depth of cure, and flexural strength were measured. Antibacterial effects of composite resins were analyzed by using Streptococcus mutans (ATCC 25175). The results were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s test (p<0.05). Results: Composite resins that contain low wt% of phytoncide demonstrated no significant difference in surface hardness, depth of cure, and flexural strength (p>0.05). However, composite resins that contain high wt% of phytoncide had significantly decreased mechanical properties (p<0.05). In terms of antibacterial effects, composite resins containing phytoncide inhibited the growth of S. mutans. Conclusions: Our findings suggest that novel composite resins containing phytoncide have effective antibacterial properties while maintaining the originally important mechanical features of composite resins.
Figures & Tables
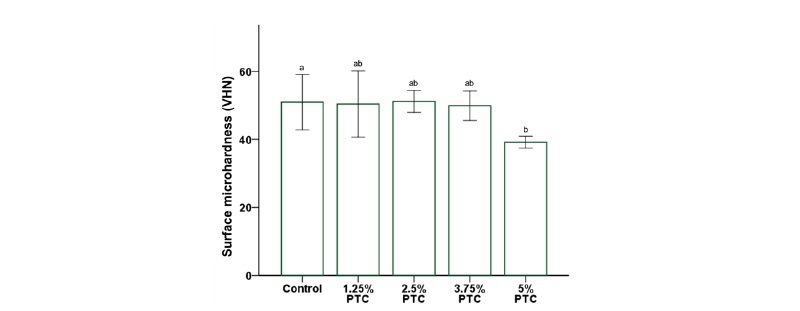
Fig. 1. Comparison of the mean surface microhardness between groups. Different letters above bars indicate significant differences(p<0.05).


