Abstract
This study aimed to examine the effects of dietary protein intake and quality on periodontal disease in Korean adults. The data used for analysis were obtained from the 7th Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016-2018). Data were analyzed using chi-square and t-test. Additionally, multiple logistic regression analysis was performed to assess the association between dietary protein intake and quality and periodontal disease. Statistical significance level was set at <0.05. Multiple logistic regression analysis of dietary protein intake and periodontal disease in the model adjusted for socioeconomic factors showed that were significantly related to the Q1 (odds ratio [OR]: 1.18, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.01-1.39). However, this correlation was not significant in the model in which all variables were corrected. Moreover, analysis of the dietary protein quality and periodontal disease in model 4, which was adjusted for socioeconomic variables, showed that were significantly related to the low score (OR: 1.13, 95% CI: 1.00-1.27). The results showed a significant association between periodontal disease and poor intake and quality of dietary protein in the Korean adult population.
Figures & Tables
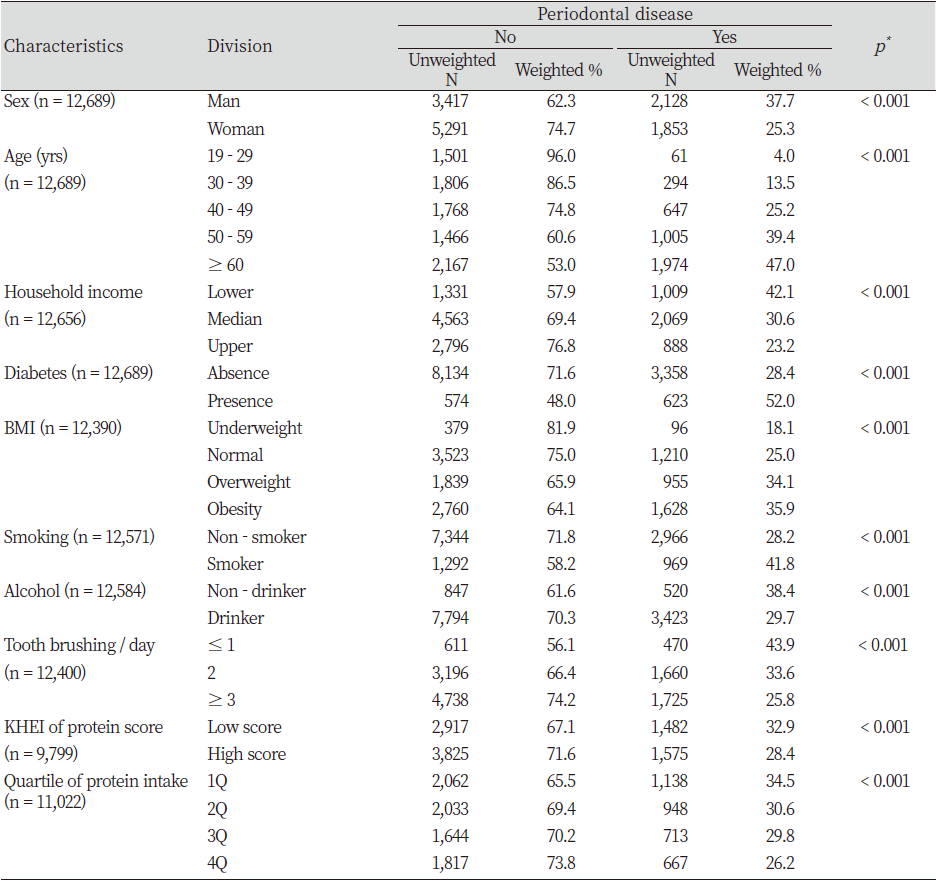
Table 1. Characteristics of the study population stratified by periodontal disease


