Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the perceived quality of classes, academic emotions, and learning achievement levels associated with the non-face-to-face classes of health science students, and to analyze the factors related to class satisfaction. Methods: Using a questionnaire, 238 health science students were surveyed regarding the quality of classes, academic emotions, and learning achievement levels. Factors related to calss satisfaction were analyzed using stepwise multiple regression. Results: Lecture types that the students were most satisfied with were ‘video lectures using PPT’ and ‘recorded lectures provided by LMS’, while ‘real-time video lectures’ were scored the lowest (p=0.005). Factors affecting non-face-to-face class satisfaction were perceived achievement (β=0.425,
Figures & Tables
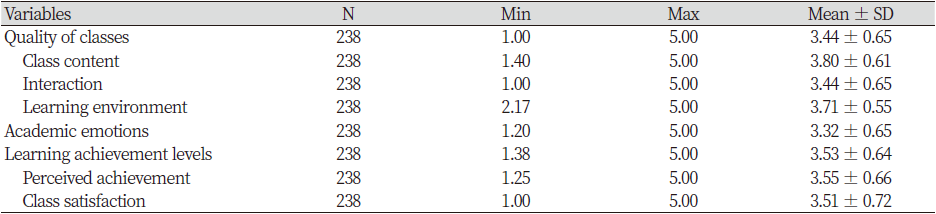
Table 1. Descriptive statistics of quality of classes, learning achievement levels, and academic emotions


