Abstract
To identify the factors influencing the turnover intention of registered South Korean dental hygienists and analyze the effect sizes. Overall, 54 studies based on criteria of PICO from 1 January 2000 to 11 January 2022 were extracted. The factors related to turnover intention were applied to the ecological system theory and categorized. Subsequently, the effect size of the correlations was comprehensively meta-analyzed by dividing it into protective and risk factors depending on the negative or positive correlation direction. For the overall effect size, the protective factor (ESr=-0.458) was higher than the risk factor (ESr=0.352). In the protective factors, organizational commitment and perceived organizational support belonging to the microsystem yielded the largest effect size. Furthermore, as for risk factors, burnout, job stress, work harassment, role conflict, and emotional labor belonging to the microsystem showed a moderate effect size. Factors belonging to the microsystem demonstrated a large effect size in both protection and risk factors for dental hygienists’ turnover intention. Additionally, the factor showing the largest effect size was protective factor categorized into a microsystem.
Figures & Tables
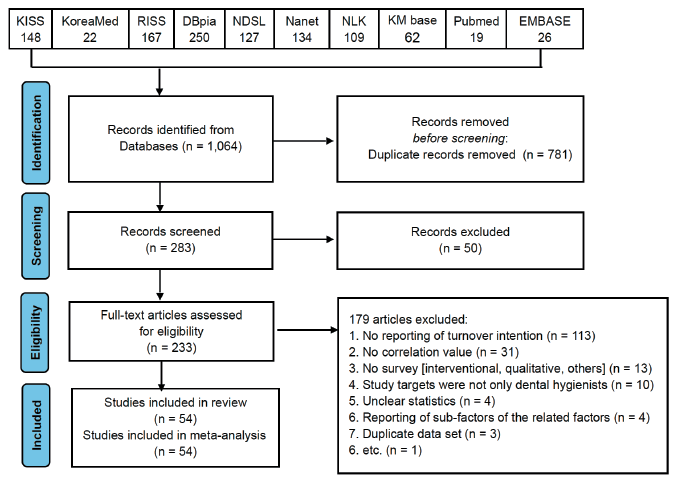
Fig. 1. PRISMA flow for the study


