Abstract
This study aimed to find a way to solve oral health inequality in old age by understanding the effect of the socioeconomic level of the elderly on oral health. We used data from the 7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. A chi-square test was performed to investigate differences in oral health according to socioeconomic status and demographic and oral health-related factors. Socioeconomic status and oral health inequality were analyzed using multiple logistic regression. The average number of teeth in the elderly was 17.20, which is insufficient for the minimum number of teeth required for mastication. In the analysis of the correlation between socioeconomic status and oral health inequality, education level, income level, and home ownership were factors influencing the oral health of the elderly; education level was found to have the strongest effect. Oral health inequality according to socioeconomic status was confirmed, and it is necessary to measure the level of oral health inequality with active efforts at the government level to resolve the gap in oral health by social class.
Figures & Tables
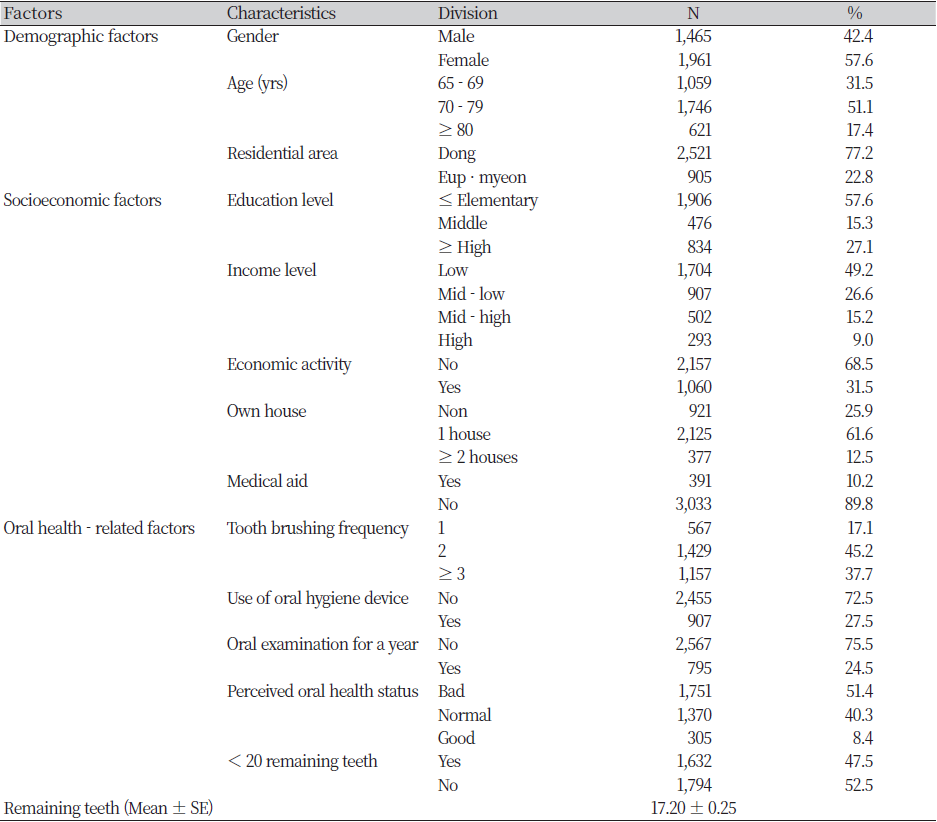
Table 1. Characteristics of the study subjects (N=3,246)


