Abstract
This study used the 2018 Korea Health Panel Survey data to analyze factors affecting employment status and income relating to unmet dental and medical care needs. Additionally it investigated measures to reduce oral health inequality among various socioeconomic classes. Descriptive statistics for the subjects’ unmet dental and medical care needs were calculated through chi-square test analysis, and multivariate logistic regression analysis was applied to identify factors affecting the unmet dental and medical care needs. The odds ratio and 95% confidence interval were calculated for each level. These data were analyzed using STATA 17.0 SE (64-bit) version, and the statistical significance level was set to
Figures & Tables
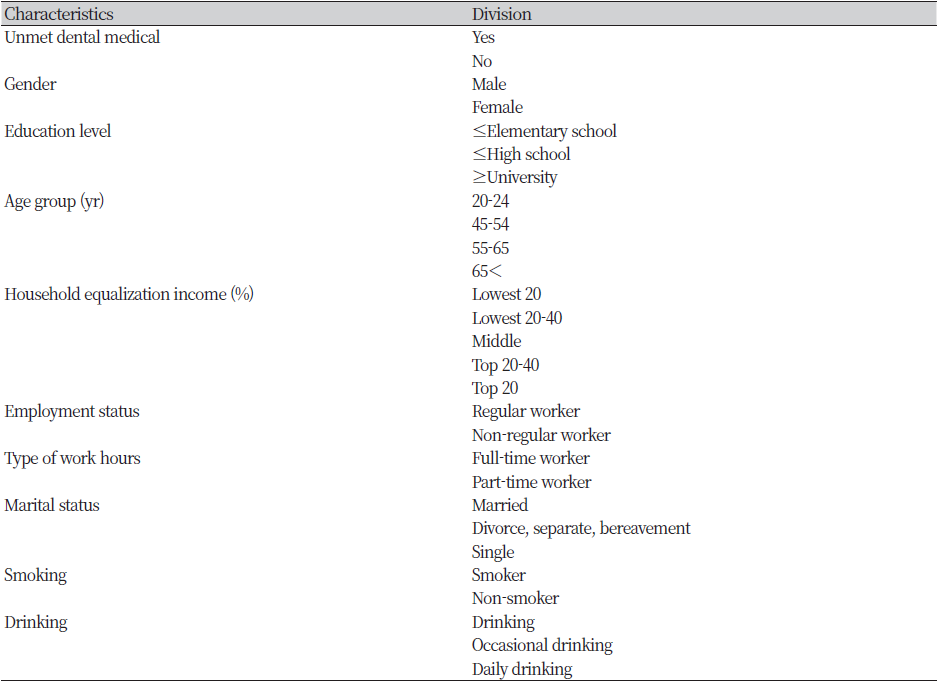
Table 1. Study variables description


