Abstract
Objectives: To compare and evaluate the degree of abrasion of the denture base resin according to the type of denture cleansers. Methods: Denture base resin specimens were prepared and dried. The resin specimens were installed in the automatic brushing machine so that the toothbrush weighed 200 g. The brushing was performed 1,000 times each, a total of 10,000 times using (1) distilled water (DW), (2) non-abrasive cleanser (NAC), and (3) toothpaste (TP), respectively. Thirty specimens were allocated for each group. The thickness of abrasion by brushing was calculated by converting the weight of the specimen. Results: In all DW, NAC, and TP groups, significant differences were found in the average amount of abrasion of the resin specimen due to 1,000 to 10,000 brushings (
Figures & Tables
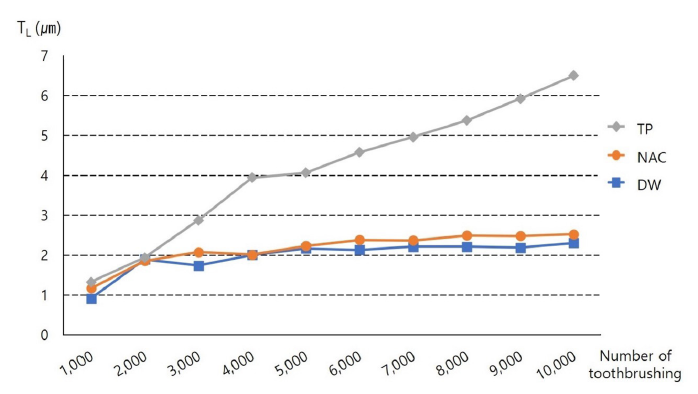
Fig. 1. The graph for change of the depth of abrasion of the specimen (T) according to the number of brushing. DW is distilled water. NAC is Non-abrasive cleanser. TP is toothpaste.


