Abstract
The aim of this study was to investigate the association between depression, anxiety, and COVID-19 with regard to dental hygienists. A questionnaire survey on depression and anxiety was conducted on 189 dental hygienists from dental hospitals and clinics in the Daegu–Gyeongbuk area. The overall prevalence of depression was 69.8% and that of anxiety was 53.4%. The aspect of depression was heavily influenced by past experience with COVID-19 related quarantine and contact with a confirmed patient. The prolonged pandemic was observed to have exerted a greater impact on depression and anxiety (
Figures & Tables
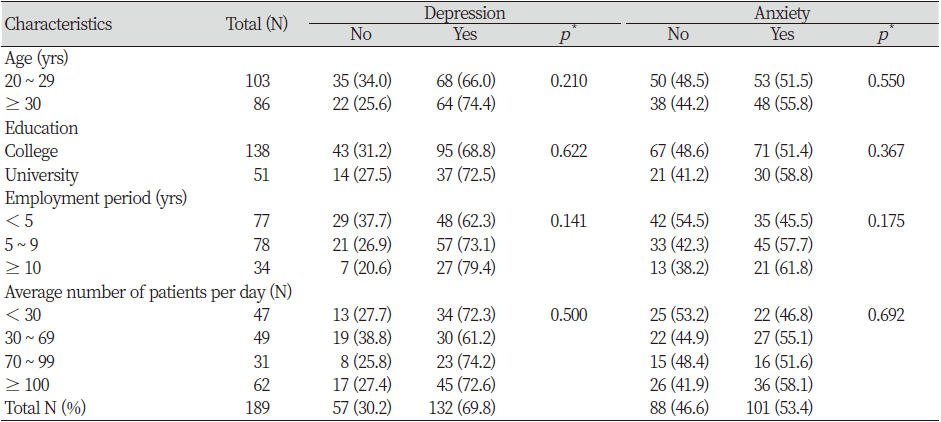
Table 1. Depression and anxiety levels according to general characteristics Unit : N(%)


